
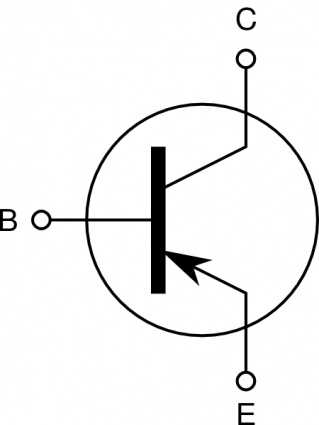
Alternatively, some of the free electrons can also be removed so electrons will flow into the transistor. For example, it can be turned into an n-type (negative type) transistor by adding free electrons, which can flow out of it easily. Silicon can be treated with impurities to make it perform in different ways.

Silicon transistors are - unsurprisingly - made from silicon. To help us understand how a transistor works, it helps to look at what they are made from. This means that a small current can switch on a larger one. When transistors are used as switches, the electric current flowing through one part of a transistor means a larger current can pass through other parts of it. Much like plugging an electric guitar into an amp, a transistor will turn a small current into a much larger one. When the transistor is being used as an amplifier, it takes an electric current and amplifies it. How a transistor works depends on whether it is being used in a transistor amplifier circuit or switch circuit. Transistors are used in everything from pacemakers, cameras, calculators, watches, hearing aids, and computers. This makes them incredibly useful for a whole host of applications. They will either block a current or let electricity pass through.Įach second, transistors turn currents on and off far faster than any human. Instead of a traditional flip switch, a transistor uses voltages to switch the circuit on and off. Transistors are unique in that they allow you to control how much current goes through a circuit. Rather than manually turning circuits on and off, a transistor will automate this process. However, this requires human interaction.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
